Background
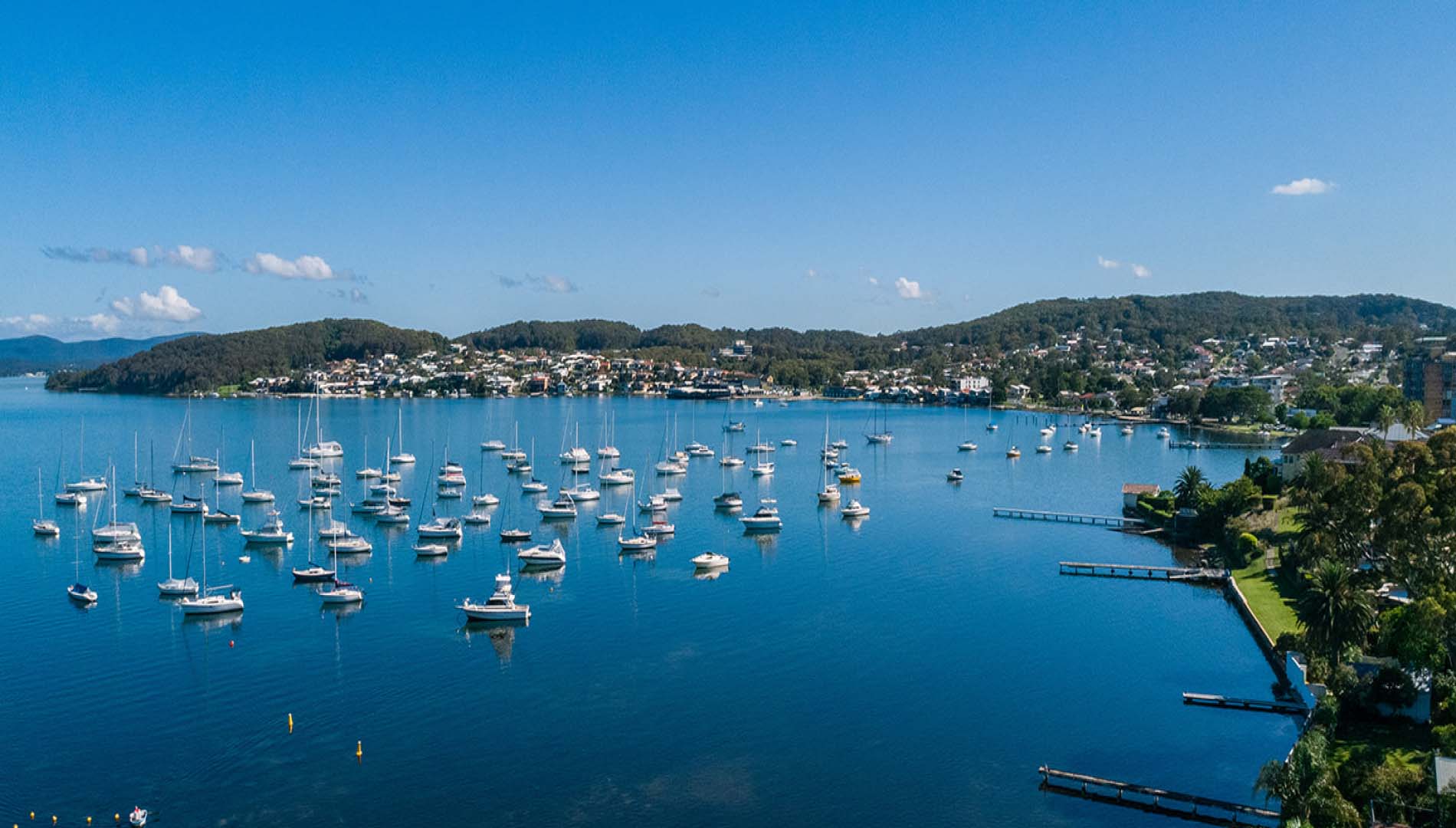
The Belmont Desalination Plant project is a significant infrastructure initiative aimed at addressing water scarcity issues by converting seawater into potable water.
Desalination is an important rainfall-independent water supply option and will help support the region and communities with a safe and reliable water source regardless of changes in weather or climate.
To provide a sustainable, reliable, and high-quality water supply through advanced desalination technology, ensuring long-term water security and resilience against climate change and drought.

Technology & Process
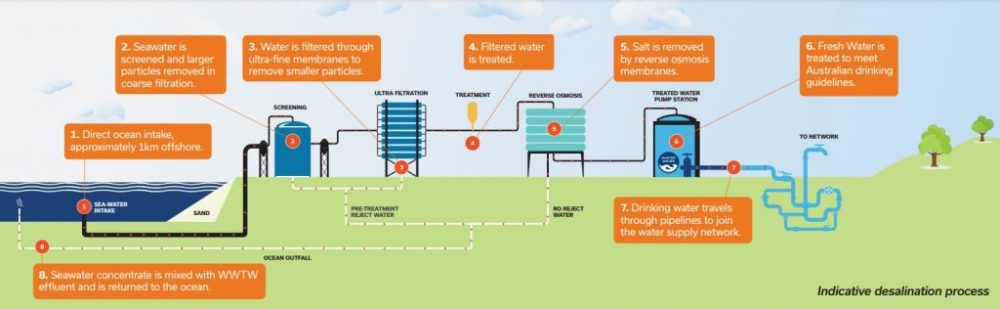
Reverse Osmosis
The plant utilizes reverse osmosis technology, a widely used and effective method for desalinating seawater. This process involves forcing seawater through semi-permeable membranes to remove salts and other impurities.
Energy Efficiency
Modern desalination plants, are designed to be energy-efficient, incorporating renewable energy sources and advanced energy recovery systems to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Environmental & Social Considerations
Environmental Impact
The project includes measures to mitigate its environmental footprint, such as careful management of brine disposal, minimizing marine life disruption, and ensuring sustainable operation.
Community Benefits
Beyond providing a stable water supply, the project can offer economic benefits through job creation during construction and operation phases, and by supporting local industries dependent on a reliable water source.
Project Implementation
Construction Phases
The project is typically implemented in stages, starting with feasibility studies, environmental impact assessments, and securing necessary permits, followed by construction, testing, and commissioning of the plant.
Public-Private Partnerships
Often, desalination projects involve collaboration between government agencies and private sector companies to leverage expertise, share risks, and ensure efficient project execution.
Challenges & Considerations
Cost
Desalination is a relatively expensive method of producing fresh water compared to traditional sources, involving high initial capital expenditure and ongoing operational costs.
Energy Consumption
Despite advancements in technology, desalination remains energy-intensive, necessitating a focus on energy-efficient processes and alternative energy sources.
Global Context
Increasing Adoption
Desalination plants are becoming increasingly common in arid regions around the world, particularly in the Middle East, Australia, and parts of the United States, as part of integrated water resource management strategies.
Technological Advances
Ongoing research and development are focused on improving the efficiency and sustainability of desalination technologies, making them more viable for widespread use.
The Belmont Desalination Plant project exemplifies the growing trend towards utilising desalination as a viable solution to global water challenges, aiming to ensure water security for future generations.